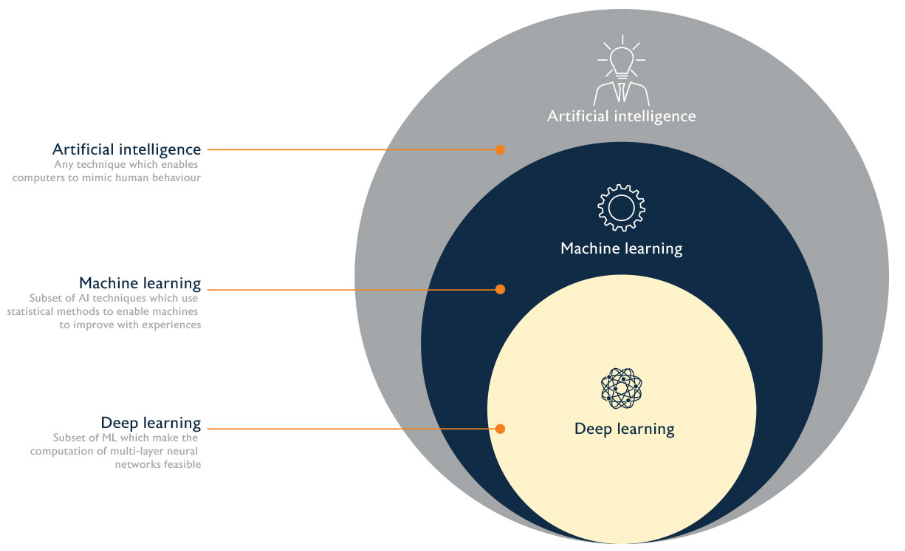
“AI is an umbrella discipline that covers everything related to making machines smarter. Machine Learning (ML) is commonly used along with AI but it is a subset of AI. ML refers to an AI system that can self-learn based on the algorithm. Systems that get smarter and smarter over time without human intervention is ML. Deep Learning (DL) is a machine learning (ML) applied to large data sets. Most AI work involves ML because intelligent behaviour requires considerable knowledge”
Artificial Intelligence
In 1955, John McCarthy, a computer scientist coined the term Artificial Intelligence. Artificial intelligence refers to the intelligence demonstrated by machines, in contrast to the natural intelligence displayed by humans and other animals. So AI makes any machine smarter. It can range from a computer program playing chess to Alexa or Siri which are capable of speech response and interpretation.
AI is of three types.
· ARTIFICIAL NARROW INTELLIGENCE(ANI)
It’s named as ANI because it
performs only one particular function. An example of this is the Deep Blue,
which was developed by IBM. It defeated Garry Kasparov, the chess grandmaster,
in 1996.
· ARTIFICIAL GENERAL INTELLIGENCE(AGI)
An AGI system is capable of
performing any task which can be completed by a human being. We are yet to
create an AGI model successfully.
·
ARTIFICIAL SUPER
INTELLIGENCE(ASI)
ASI is a term that often scares people because it refers to machines superseding humans. It has not happened, but Stephen Hawking did warm about it.
Machine Learning
Machine
Learning is a subcategory of Artificial Intelligence. Arthur Samuel coined the
term ‘machine learning’ in 1959. Basically, it is a field of artificial
intelligence that uses statistical techniques to give computer systems the
ability to “learn” from data, without being explicitly programmed. The name
machine learning was coined in 1959 by Arthur Samuel.
The key idea behind ML is that
machines are capable of learning and becoming smarter on their own by accessing
and analyzing different types of data.
It is fast becoming the handiest
type of technology of any kind of business with its quick integration. ML
models can easily read huge sets of data and make predictions based on the
recognition of these complex data sets and patterns. It can perform multiple
activities like speech recognition, facial recognition, translation, object
recognition etc.
One of the most unique features
of Machine Learning is its capability to adjust and respond depending on the
data which they are exposed to. This way it even eliminates the need for human
intervention as long as the data keeps flowing.
Deep Learning
Deep learning is part of a broader family of
machine learning methods based on learning data representations, as opposed to
task-specific algorithms. DL refers to the deep artificial neural networks or
the layers of the neural network. Deep artificial neural networks are basically
algorithm sets which provide accurate solutions for problems like sound
recognition, image recognition, recommender systems, etc. They require large
amounts of labelled data and substantial computing power as well.
Learning can be supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised. While training an algorithm in supervised learning, a full set of labelled data has to be provided.
In unsupervised learning, a deep learning model is provided with a dataset. This dataset is without any specific instructions on what to do with it. The sample dataset is a collection of examples without any particular desired outcome or correct answer. It is the task of the neural network to automatically find structure in that data by extracting only the useful features and analyzing its structure.
Lastly, semi-supervised learning is nothing more than a training dataset with both labelled and unlabeled data. When one has to extract certain relevant features from a dataset and labelling becomes a time-taking task then this method is quite useful. It uses a bit of both for the desired outcome.
Source : globaltechcouncil.org